Silo Discharge to Container
Discharging bulk materials from silos directly into intermodal containers is a critical operation for facilities involved in bulk export, long-distance transport, or temporary off-site storage. This method allows powders and granulates like cement, fly ash, plastic pellets, or food ingredients to be transferred efficiently into containers with minimal handling, ensuring material integrity and compliance with transport regulations.
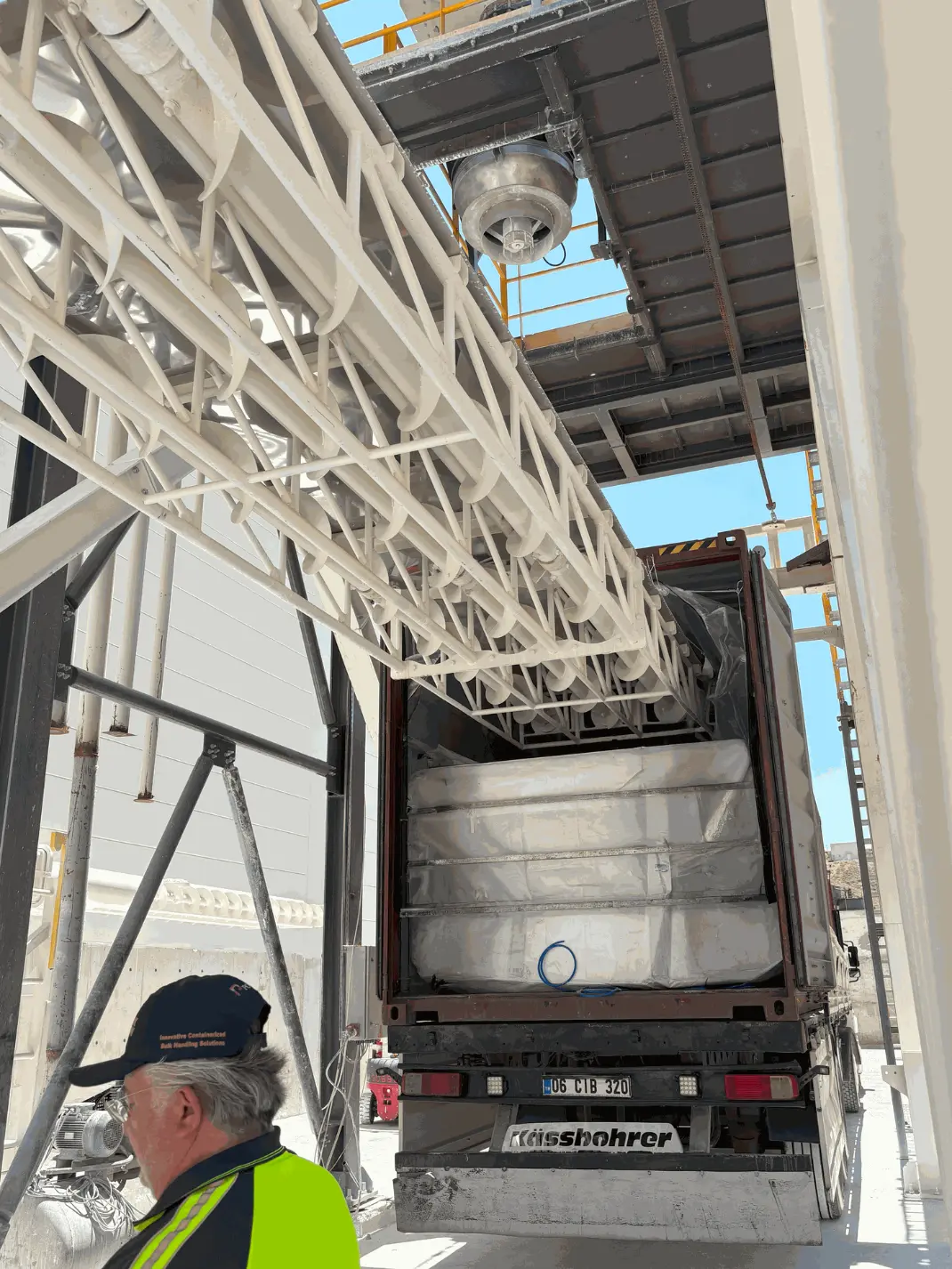

How the System Operates
• Container Setup & Positioning: Before filling begins, the container must be securely aligned with the silo outlet to ensure efficient material flow and minimize spillage. Containers used for bulk solid loading are generally lined and reinforced to prevent contamination and maintain product integrity during transport.
• Connection & Sealing: A telescopic chute is installed into the container opening to ensure a sealed connection. This mechanism prevents dust emissions and spillage during the loading process.
• Controlled Discharge: Material flows from the silo into the container by equipment such as rotary valves, screw conveyors, or pneumatic conveyors, depending on flow characteristics and required throughput.
• Monitoring & Termination: Operators use level indicators, cameras, or weighing platforms to monitor the bulk material filling progress. Once the target weight or volume is reached, the system automatically stops discharge.
• Dust Control & Safety: Dust collection systems (integrated into the loading bellows) filter displaced air during filling. Grounding systems and overfill protection devices may also be installed to enhance safety.
Key Components
• Telescopic Chutes: Enginered for efficient, secure and dust-free container loading. Often include integrated dust collection and retraction systems.
• Discharge Valves & Flow Control Devices: Rotary valves, slide gates, or screw conveyors ensure a consistent, controllable material flow into the container.
• Weighing Systems or Load Monitoring: Load cells or weighing platforms provide accurate measurement of the material being loaded, preventing underfilling or overloading.
• Container Liners & Bulkhead Fittings: For powders and fine materials, liners protect contents from contamination and moisture, and ensure smooth unloading at the destination.
• Dust Collection Equipment: High-efficiency filters minimize dust release and keep the working environment clean and compliant.

Advantages & Benefits of Silo Discharge to Container
• Direct Loading for Shipment or Storage: Eliminates intermediate packaging or handling steps. Bulk material moves directly from silo to logistics chain.
• Dust-Free Operation: Sealed transfer systems are designed to contain fine particles, minimizing dust emissions during handling. This mechanism not only prevents product loss but also promotes a cleaner and safer working environment.
• Efficient Use of Time & Space: Container loading systems are compact and allow fast, repeatable operations for efficient and sustainable applications.
• Flexible Configuration: Compatible with different container types (lined, open-top, ISO tanks) and a wide range of materials.

Industry-Specific Examples
• Cement & Minerals: Fine powders like cement or fly ash are loaded into containers by fluidizing discharge cones and sealed spouts. Moisture protection and dust control are critical in these processes.
• Food & Beverage: Flour, sugar, or starch is transferred into food-grade containers using stainless steel loading chutes and hygienic liners. Equipment is designed for easy cleanability.
• Plastics & Polymers: Plastic pellets are loaded into antistatic-lined containers to prevent electrostatic discharge and material degradation during transport.
• Chemical & Specialty Materials: ATEX-compliant systems handle fine, hazardous, or temperature-sensitive materials. Dust collection systems, safety mechanisms, and flow control devices are integrated into the loading setup.